

If the two weights disagree, you continue heating and weighing until you gets weights that agree. If the two weights are in agreement, then you are done heating. H 2O -> 0.43 g / 18.015 g/mol = 0.0239 molĬoCl 2 -> 0.01194 mol / 0.01194 mol = 1ĥ) How can you make sure that all of the water of hydration has been removed?Īfter weighing the anhydrous CoCl 2, you would continue to heat it. What is the formula for the original hydrate? How can you make sure that all of the water of hydration has been removed?Ģ) Determine moles of anhydrous CoCl 2 and H 2O:ĬoCl 2 -> 1.55 g / 129.839 g/mol = 0.01194 mol When cooled, the mass of the remaining dehydrated compound is found to be 1.55 g. Problem #4: A 1.98 g sample of a cobalt(II) chloride hydrate is heated over a burner. What is the value of n in the hydrate's formula?ġ) Calculate moles of anhydrous barium chloride: After heating, 4.26 g of anhydrous barium chloride, BaCl 2, remains.

Spokesperson (Optional, for groups with 5 students) Leads the team in analyzing the data and the experimental error.Leads the team in developing experimental procedures.Leads the team in developing the theoretical foundations of the science behind the experiment.Responsible for formulating the purpose and the goal of the experiment.Validates group members have the supplies.Responsible for the Safety component in all aspects of the experiment.Responsible for ensuring that all team members are present and actively participating according to their roles.Roles will rotate from lab to lab in alphabetical order. Insufficient heating to cause all water to escape (how do you determine the process is complete?)Įach member of your team will have a role for the experimental design assignment.
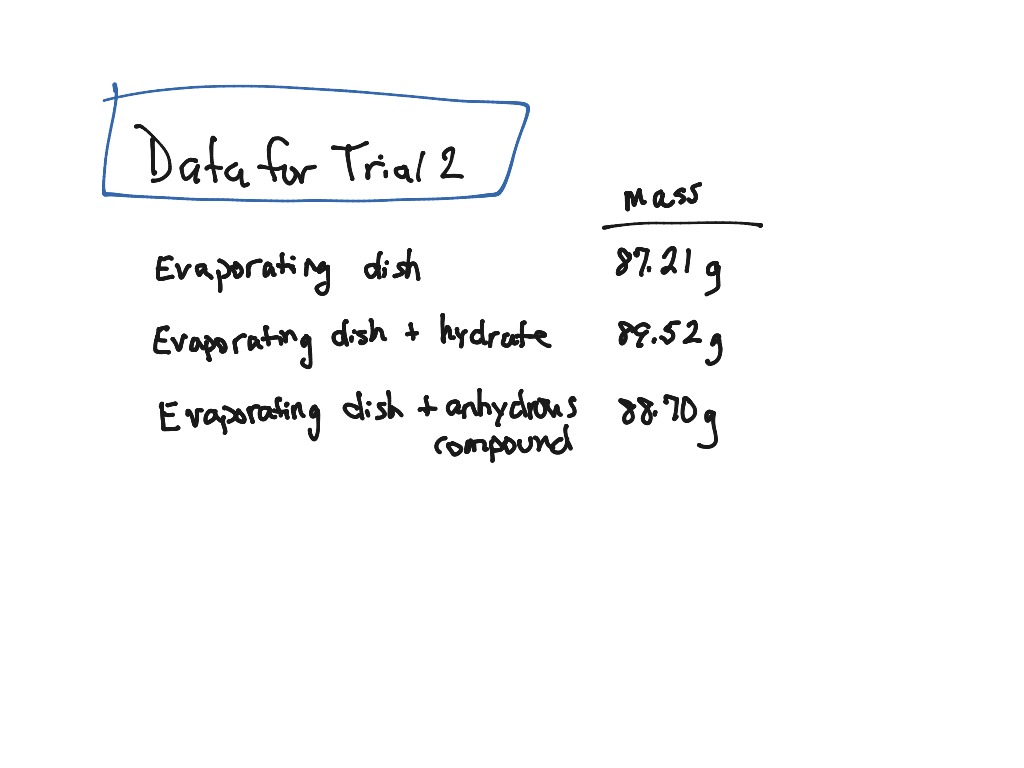

Spattering of sample upon heating as water escapes from hydrated salt.Humidity, water adsorbed to surface materials.Parameters you need to account for in your proposal: You can substitute aluminum pie pans for aluminum foil. \( \newcommand\]įor your experiment design use the supplies mentioned above.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
